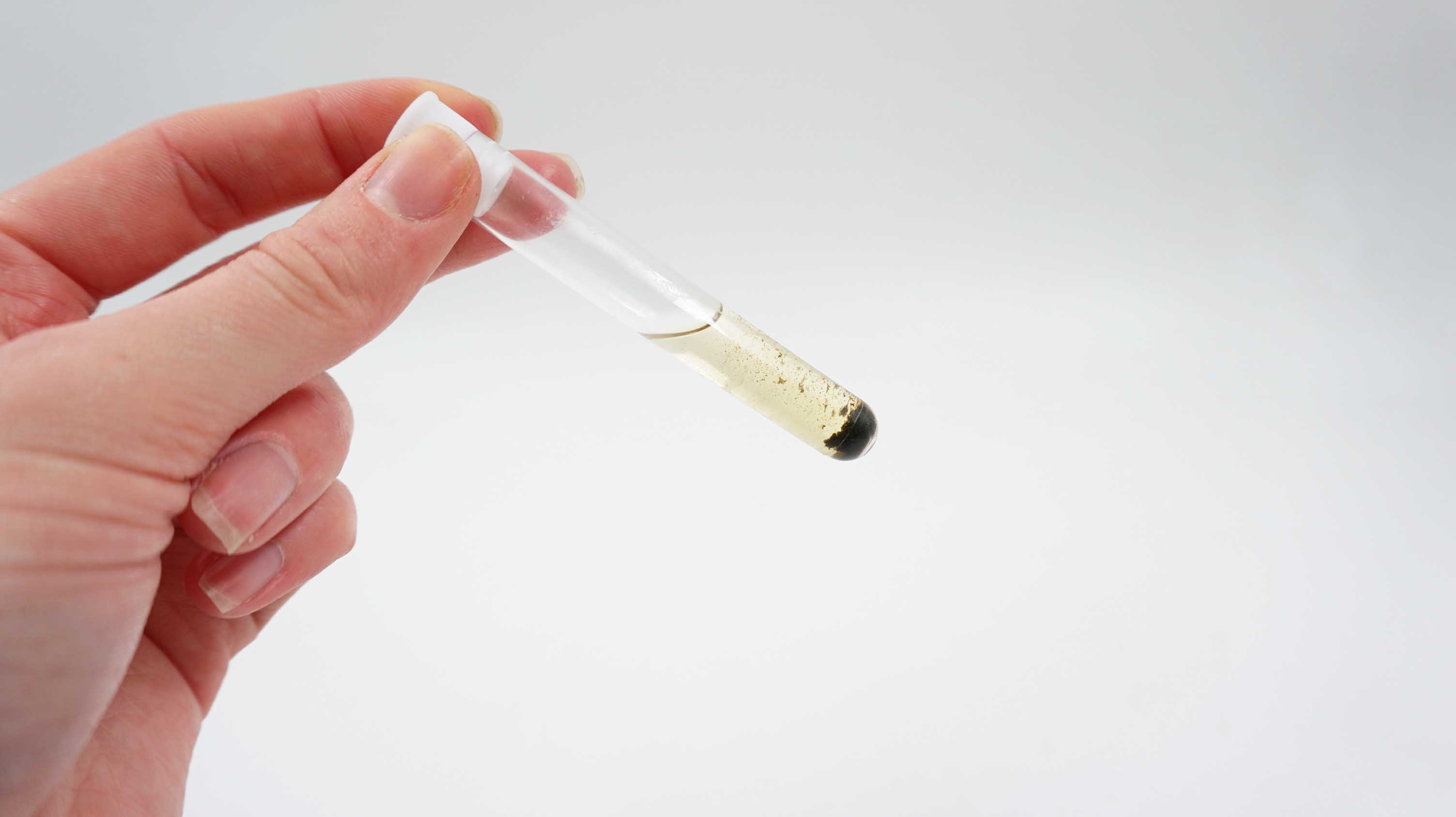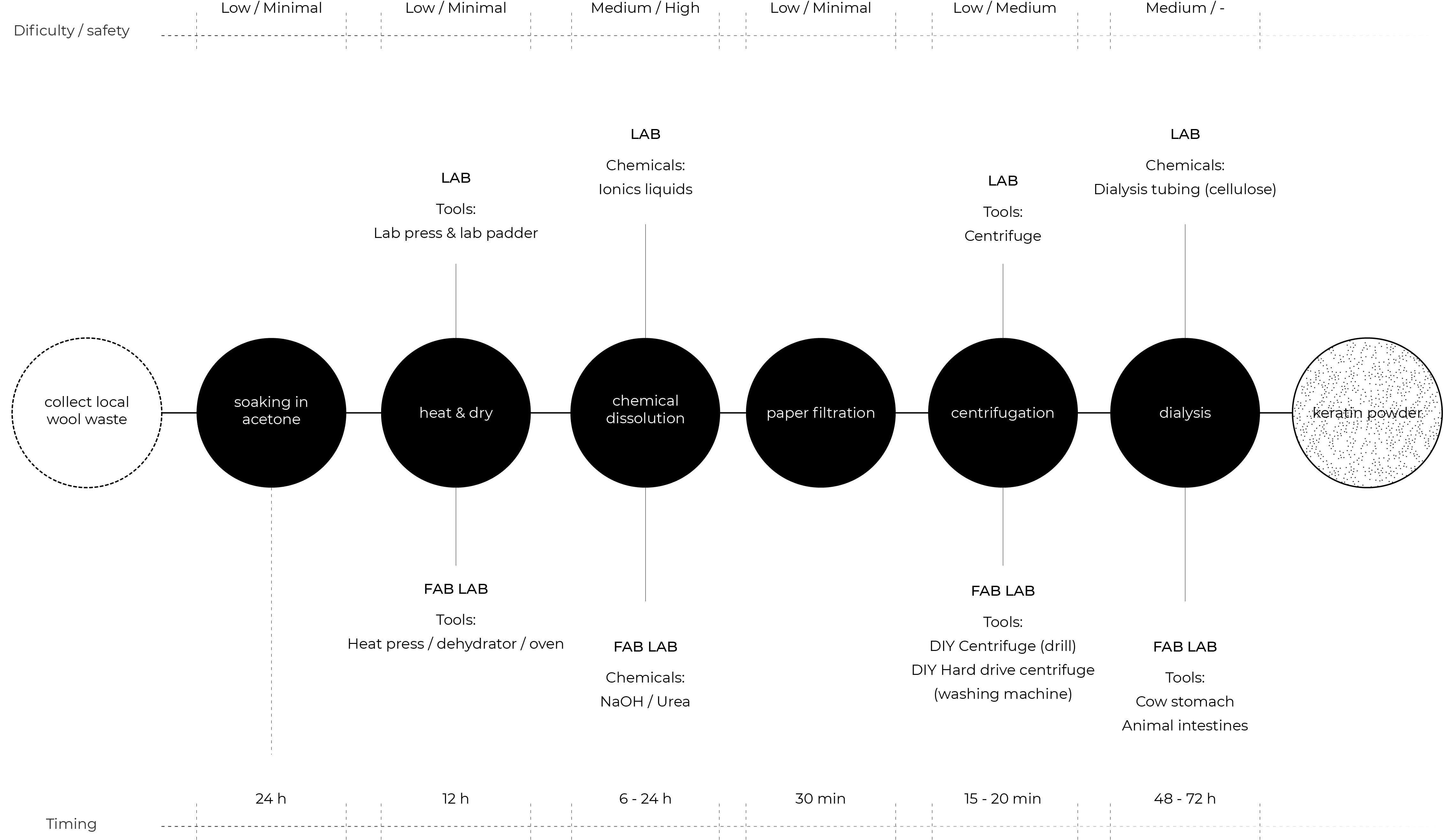
- Wool pretreatment
- Chemical dissolution
- Filtration
- Centrifugation
- Biuret reagent
- Dialysis
- Freeze-drying
1. WOOL PRETREATMENT
| Timing |
Difficulty |
Safety |
| 25 h |
Low |
Low |
- OPTION 01: Soxhlet extraction set, measuring cups, spoon, oven, plastic bags
- OPTION 02: Lab padder, lab press, measuring cups, spoon, oven, plastic bags
- OPTION 03: Cooking roller, heatpress, dehydrator / oven, measuring cups, spoon, plastic bags (zipper)
Composite
| a. |
b. |
c. |
| Acetone / Ethanol |
Distilled Water |
Wool |
| 200 ml |
50 ml |
50 g |
- You can reuse the concentration.
Materials description
ACETONE
Acetone, propanone or dimethyl ketone, is an organic compound with the formula C3H6O. It is a colourless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odour. Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important organic solvent in its own right, in industry, home, and laboratory.
| Chemical formula |
Melting point |
Molar mass |
Density |
Appearance |
Solubility in water |
| C3H6O |
-95°C |
58,08 g/mol |
784 kg/m³ |
colourless liquid |
miscible |
ETHANOL
is an organic chemical compound. It is a simple alcohol with the chemical formula C2H6O. Ethanol is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation of sugars by yeasts or via petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. It has medical applications as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the synthesis of organic compounds. Ethanol is a fuel source.
| Chemical formula |
Melting point |
Molar mass |
Density |
Appearance |
Solubility in water |
| C2H6O |
−114.14 ± 0.03°C |
46.069 g·mol−1 |
0.78945 g/cm³ |
colourless liquid |
miscible |
Process
OPTION 01 - IN THE LAB
- Clean the wool with acetone or ethanol mixture solvent in Soxhlet extraction set for 48 h.
- Then rinse it in distilled water and dry at 100°C for 12 h in an oven.
OPTION 03 - IN FABLAB
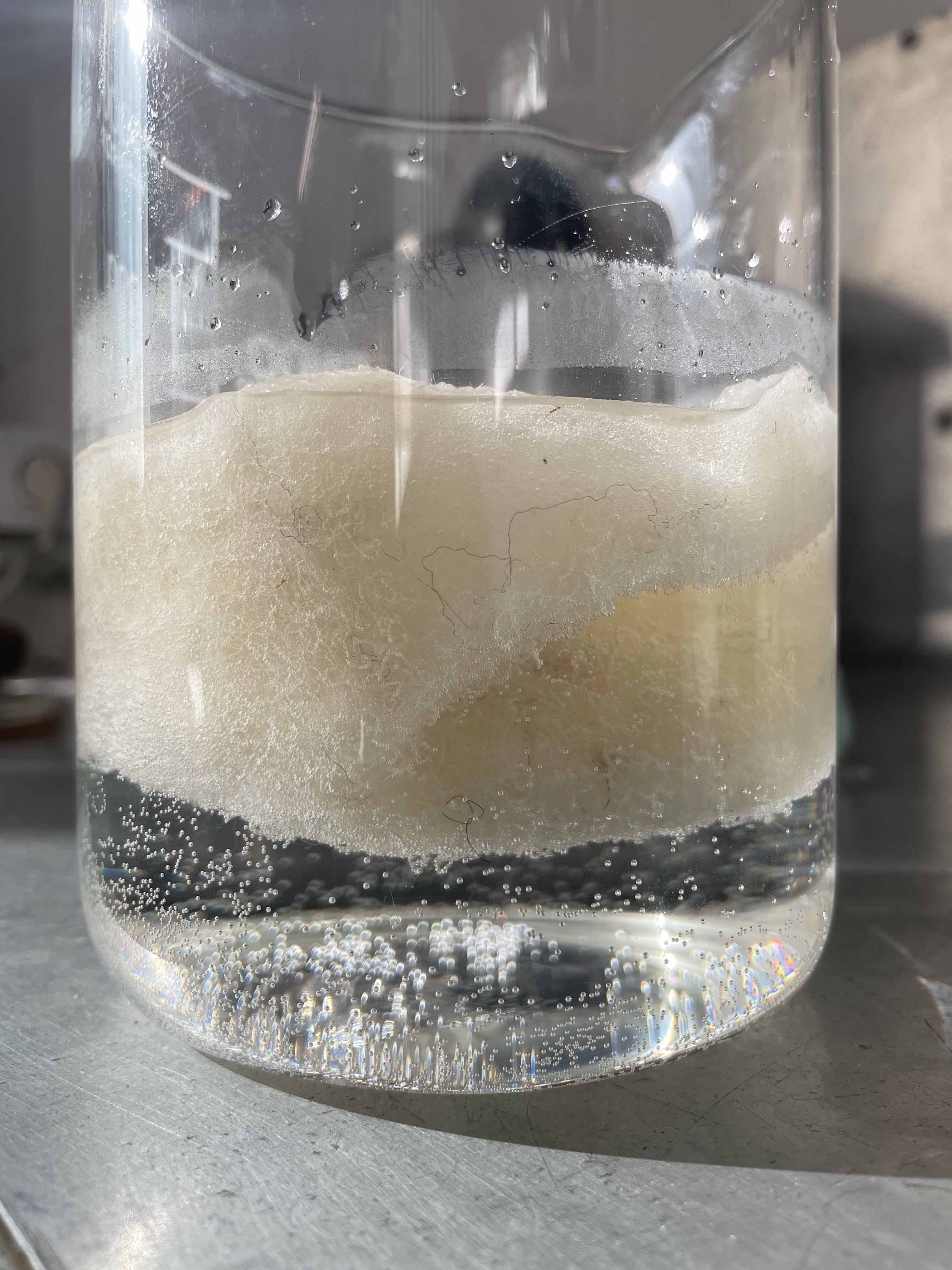

2. CHEMICAL DISSOLUTION
| Timing |
Difficulty |
Safety |
| 6 - 24 h |
Medium |
High |
Important facts
- preheating magnetic stirrer, protective gloves, protective glasses, lab coat, measuring cups (lab), magnet, weight, spoon, funnel, kettle
Materials description
UREA
also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula CH₄N₂O. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen (N) and is an important raw material for the chemical industry.
| Chemical formula |
Melting point |
Molar mass |
Density |
Systematic name |
Appearance |
Solubility in water |
| CH₄N₂O |
182 °C |
76,12 g/mol |
1.32 g/cm³ |
thiokarbonyldiamid |
white solid |
545 g/L (at 25 °C) |

M-BISULFATE
Sodium bisulfate is an acid salt formed by partial neutralization of sulfuric acid by an equivalent of sodium base, typically in the form of either sodium hydroxide (lye) or sodium chloride (table salt).
| Chemical formula |
Melting point |
Molar mass |
Density |
Appearance |
Solubility in water |
| NaHSO₄ |
58.5°C |
120.06 g/mol (anhydrous); 138.07 g/mol (monohydrate) |
2.742 g/cm3 (anhydrous); 1.8 g/cm3 (monohydrate) |
white solid |
28.5 g/100 mL (25 °C) ; 100 g/100 mL (100 °C) |
SODIUM HYDROXIDE
caustic soda - is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound. Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and alkali that decomposes proteins at ordinary ambient temperatures and may cause severe chemical burns. It is highly soluble in water, and readily absorbs moisture and carbon dioxide from the air. Sodium hydroxide is used in many industries: in the manufacture of pulp and paper, textiles, drinking water, soaps and detergents, and as a drain cleaner.
| Chemical formula |
Melting point |
Molar mass |
Density |
Appearance |
Solubility in water |
| NaOH |
323°C |
39.9971 g mol−1 |
2.13 g/cm³ |
white, hard (when pure), opaque crystals |
418 g/L (0 °C); 1000 g/L (25 °C); 3370 g/L (100 °C) |

Composite
| a. |
b. |
c. |
d. |
e. |
| Urea |
M-bisulfite |
NaOH |
Distilled Water |
Wool |
| 8 % |
0,5 % |
1 % |
90,5 % |
- |
| 54 g |
3 g |
6 g |
600 ml |
10 g |
Process
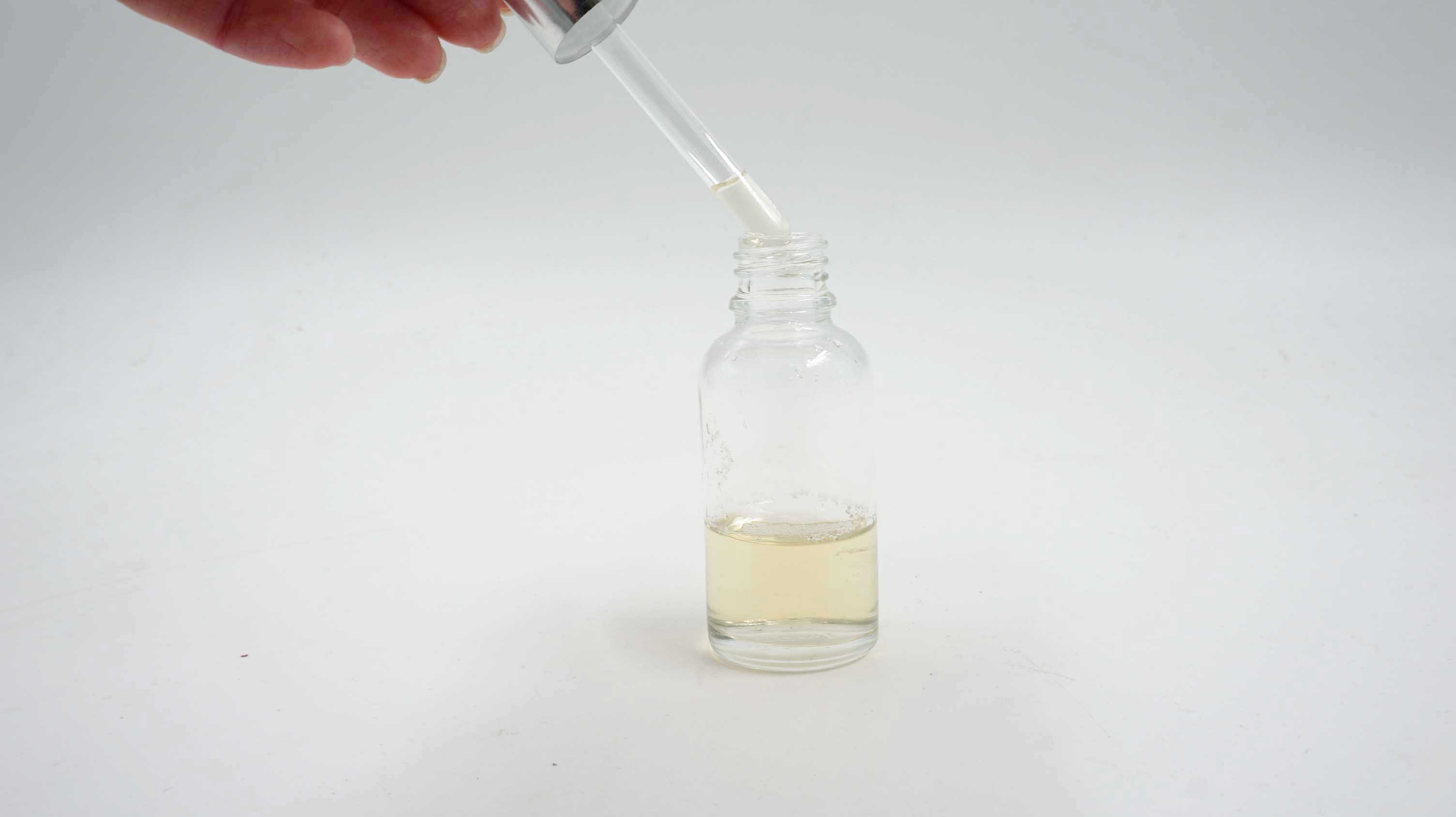

Conclusion
| a. Initial quantity |
b. Extracted |
c. Filtrated |
| 600 ml |
300 ml |
290 ml |
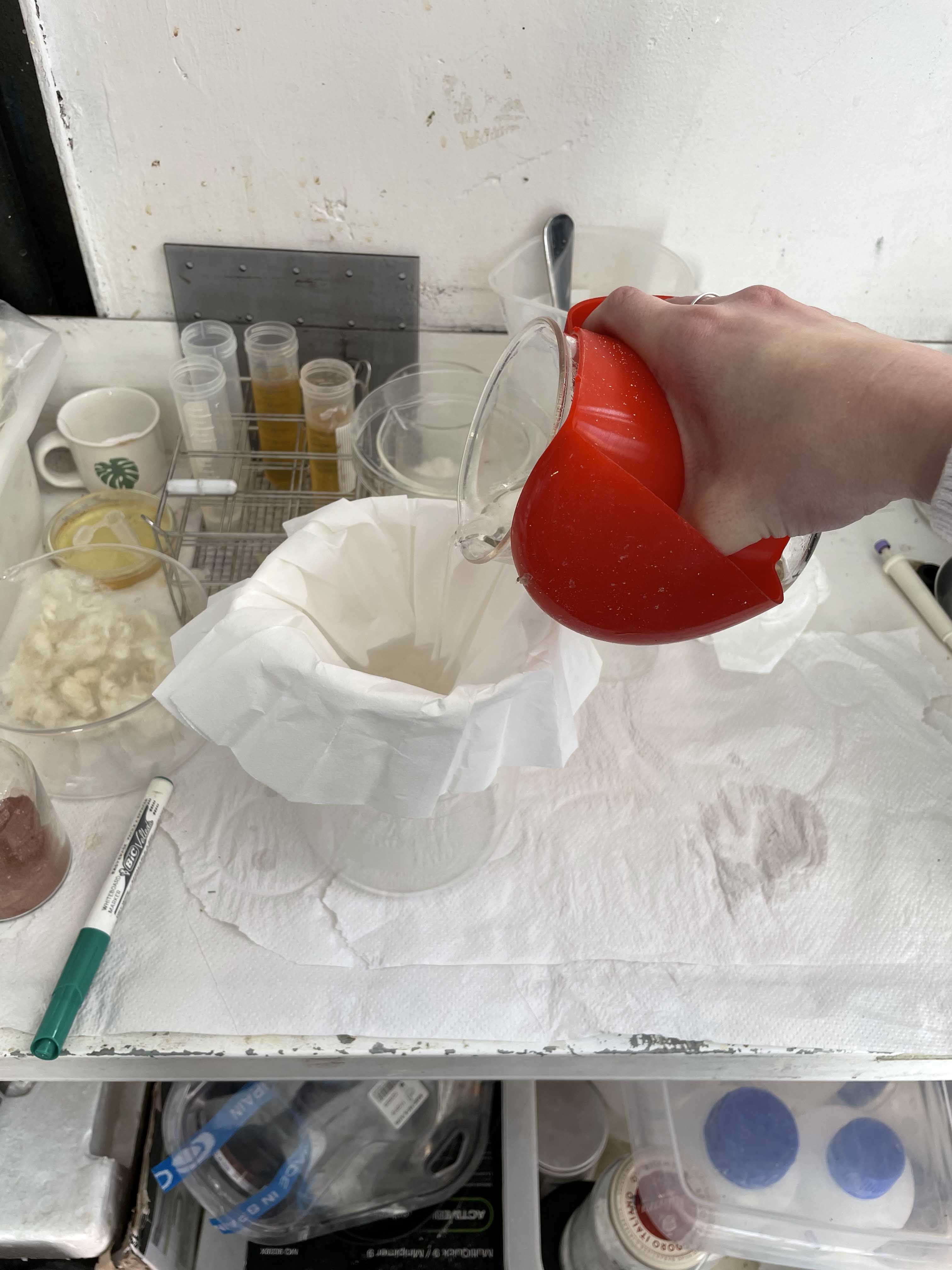
3. FILTRATION
| Timing |
Difficulty |
Safety |
| 1 h |
Low |
Low |
- paper filters (better folded ones - coffee filters did not work out in this case), lab glass jar, funnel
Process
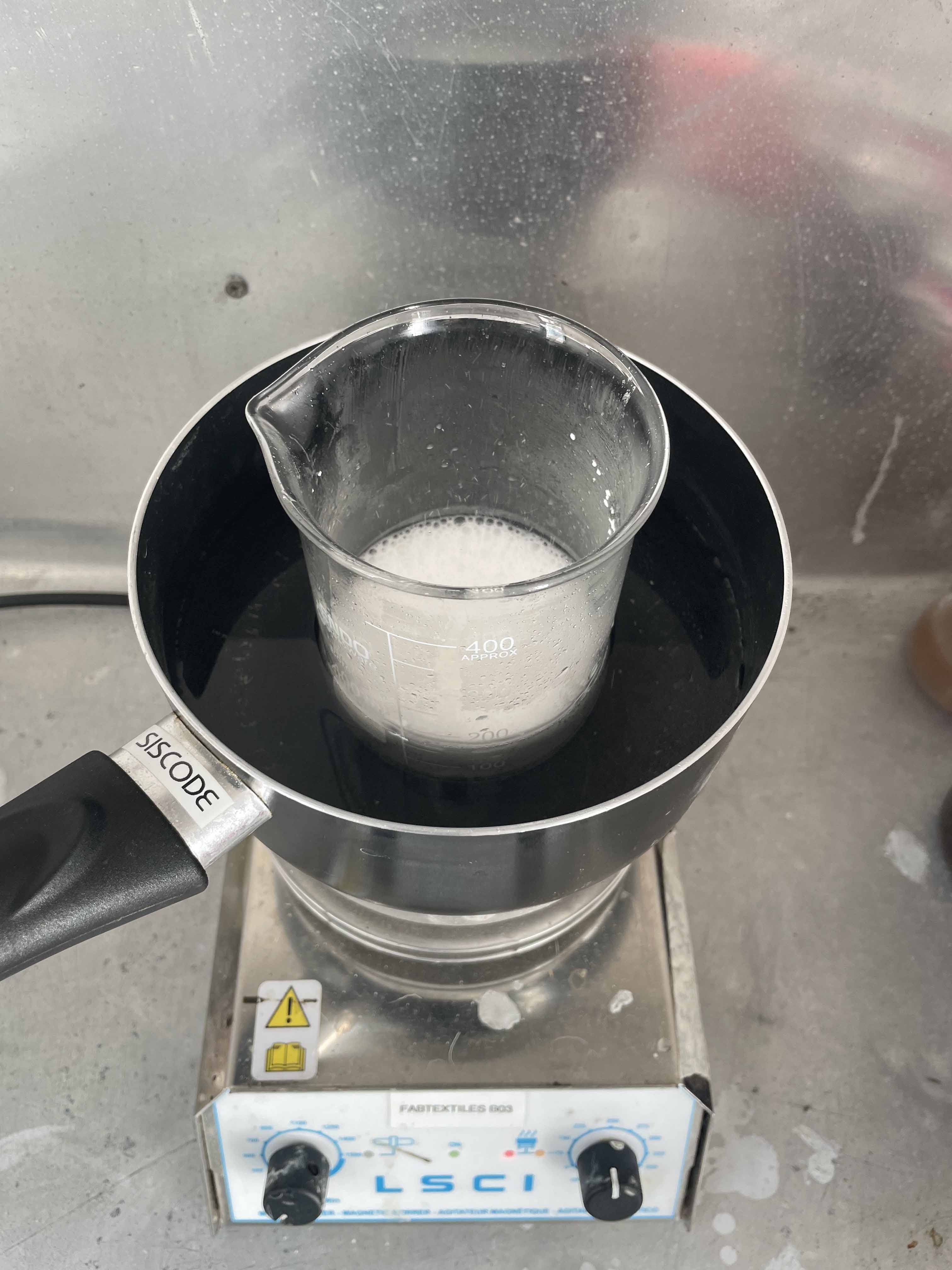
4. CENTRIFUGE
| Timing |
Difficulty |
Safety |
| 15-20 min |
Low |
Medium |
- lab tubes for centrifugation (25 ml with a cover), drill, 3D printed holder, screws, protective glasses, syringe
Process
Conclusion
- You have to properly stabilize the 3D print to the drill - avoid excessive torque. The lab tubes must be properly stabilized.
5. BIURET REAGENT
| Timing |
Difficulty |
Safety |
| 1 - 48 h |
Medium |
Low |
- weight, measuring cups, spoon, cokng stove / oven, 2 x cooking pots, paper filters, plate (for crystallzation), spoon, bottle (for the biuret solution), kettle
Composite of Biuret reagent
| a. |
b. |
c. |
d. |
| Copper sulphate |
Sodium potassium tartarate (Rochelle salt) |
NaOH |
Distilled water |
| 1,5 g |
6 g (in 500 ml of water) |
23,4 g |
1 l |
| Chemical formula |
Melting point |
Molar mass |
Density |
Appearance |
Solubility in water |
| CuSO₄ |
110°C |
159,609 g/mol |
3.60 g/cm³ |
grey-white, blue |
1.055 molal (10 °C) |
- Sodium potassium tartarate - Rochelle salt
| Chemical formula |
Melting point |
Molar mass |
Density |
Appearance |
Solubility in water |
| KNaC₄H₄O₆·4H2O |
75°C |
282.1 g/mol |
1.79 g/cm³ |
Colorless, odorless monoclinic needles |
26 g/100 mL (0°C); 66 g /100 mL(26°C) |
Potassium bitartrate - also known as potassium hydrogen tartrate, is a byproduct of winemaking. In cooking, it is known as cream of tartar. It is processed from the potassium acid salt of tartaric acid. The resulting powdery base can be used in baking or as a cleaning solution (when mixed with an acidic solution such as lemon juice or white vinegar).
| Chemical formula |
Melting point |
Molar mass |
Density |
Appearance |
Solubility in water |
| KC₄H5O₆ |
- |
188.177 g/mol |
1.05 g/cm³ (solid) |
White crystalline powder |
0.57 g/100ml (20°C) |
In case that you do not have sodium potassium tartarate called also Rochelle salt, you can do it on your own. Following the recipe below.
Process
- Mix the copper sulphate with Rochelle salts in 500 ml of cold distilled water. Till it will completely disolved.
- Beside prepare solution of Sodium hydroxide - 2 Ml of NaOh : 375 ml of distilled water (hot).
1 L of 2.00 M NaOH solution contains 2.00 x (23.0 + 16.0 + 1.0) g NaOH --> 500 ml of 2.00 M NaOH solution contains 80 / 2 g NaOH = 40.0 g of NaOH
- Let the soluion of sodium hydroxid to cool down.
- Mix both the solution NaOH and copper sulphate in volumetric flask and make it final volume to 1000 ml by adding distilled water.
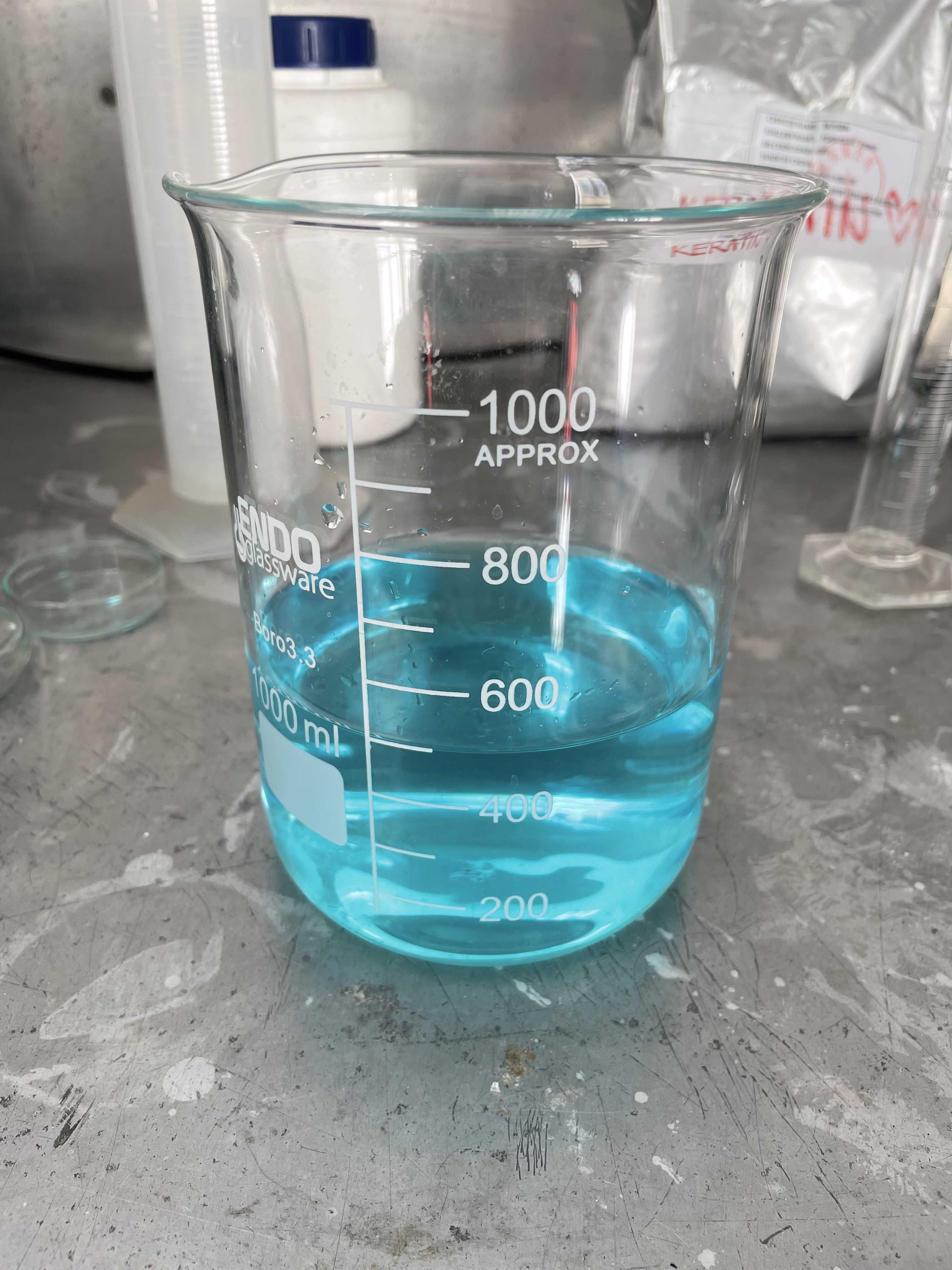
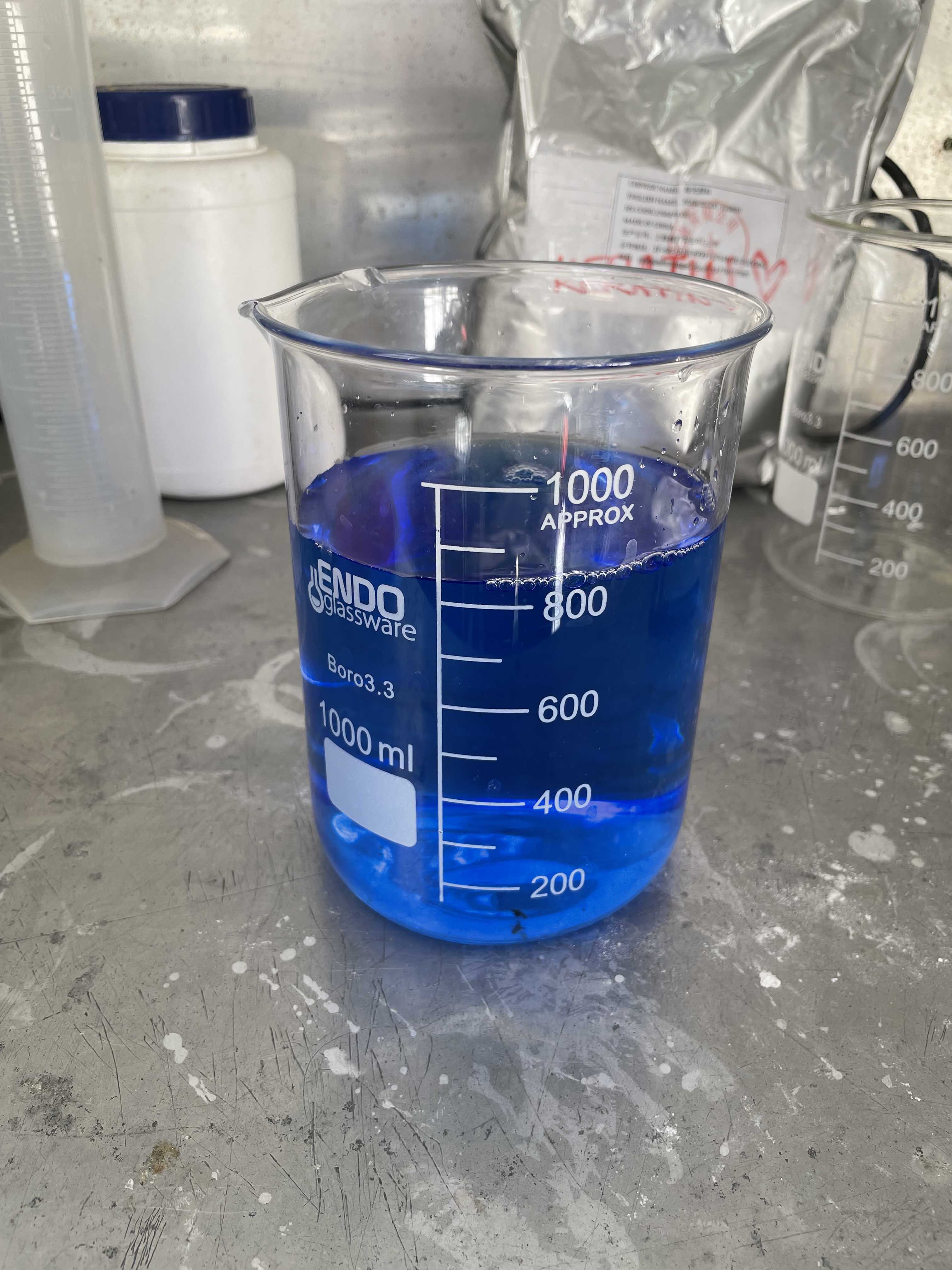


Composite of Rochelle salts
- If you start with 500 g of baking soda or washing soda and 200 g of cream of tartar, you should collect around 210 grams of Rochelle salt.
| a. |
b. |
c. |
| Baking soda or Washing soda |
Cream of tartar |
Distilled water (hot) |
| 500 g |
145 g |
200 ml |
Process
- Place a pot on a cooking stove on the highest temperature and add baking soda. Keep stirring for 20-30 min.
- Let the baking soda cool down and in the meantime prepare solution of cream of tartar.
- Place one pot with water on the cooking stove and add a glass jar into it - to create a bath. Pour destilled water into the jar and preheat it a little.
- After you can slowly add the cream of tartar. Stir it properly.
- One by one with a spoon add the baking soda into the pot. A chemical reaction will appear. Do it slowly and wait till the reaction will sttol tto add another spoon.
- Add more baking soda till you will see that no reaction appears again. What means that the solution is "full enough".
- Also the white creamy solution of the cream of tartar will become transparent.
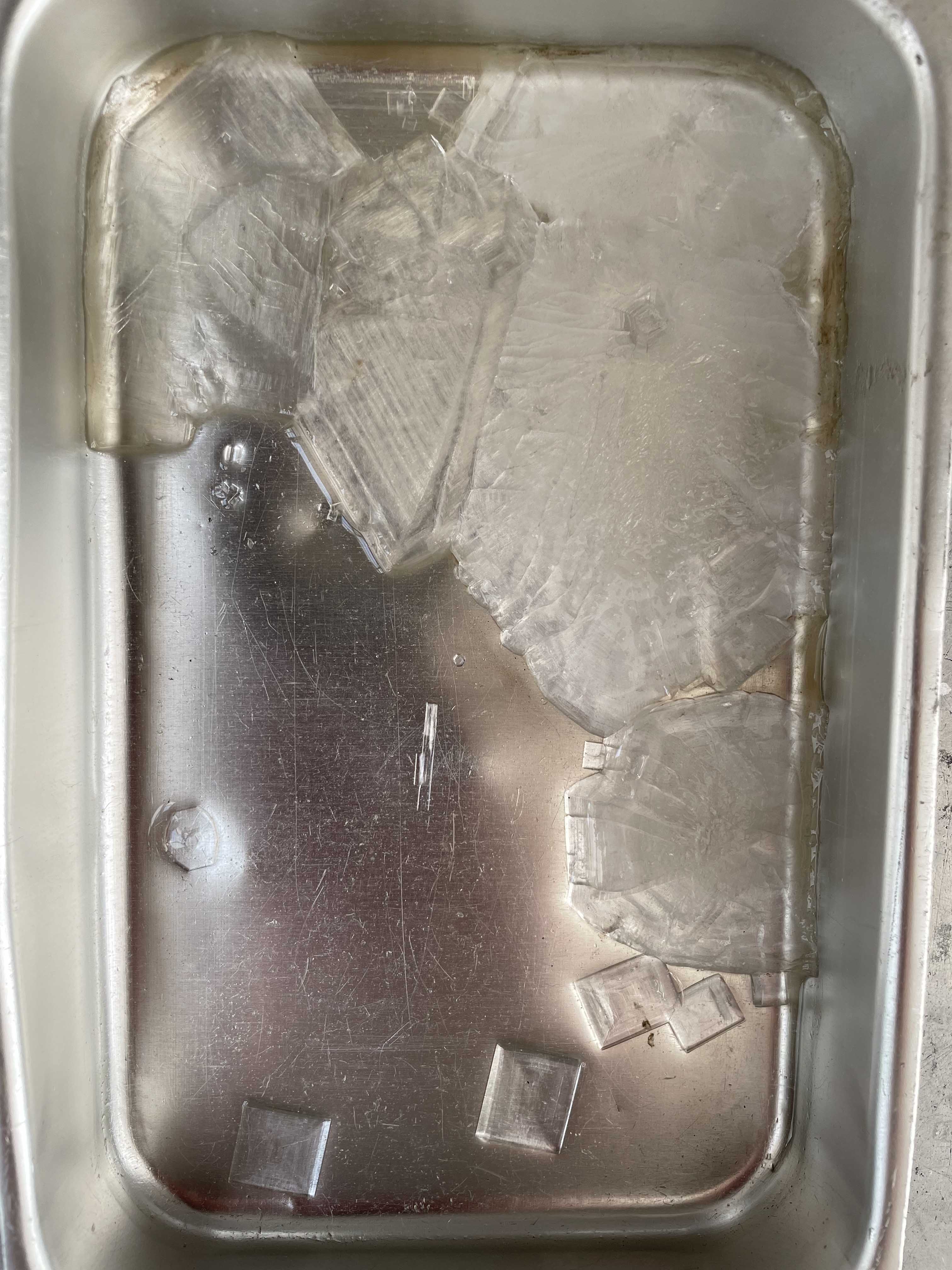
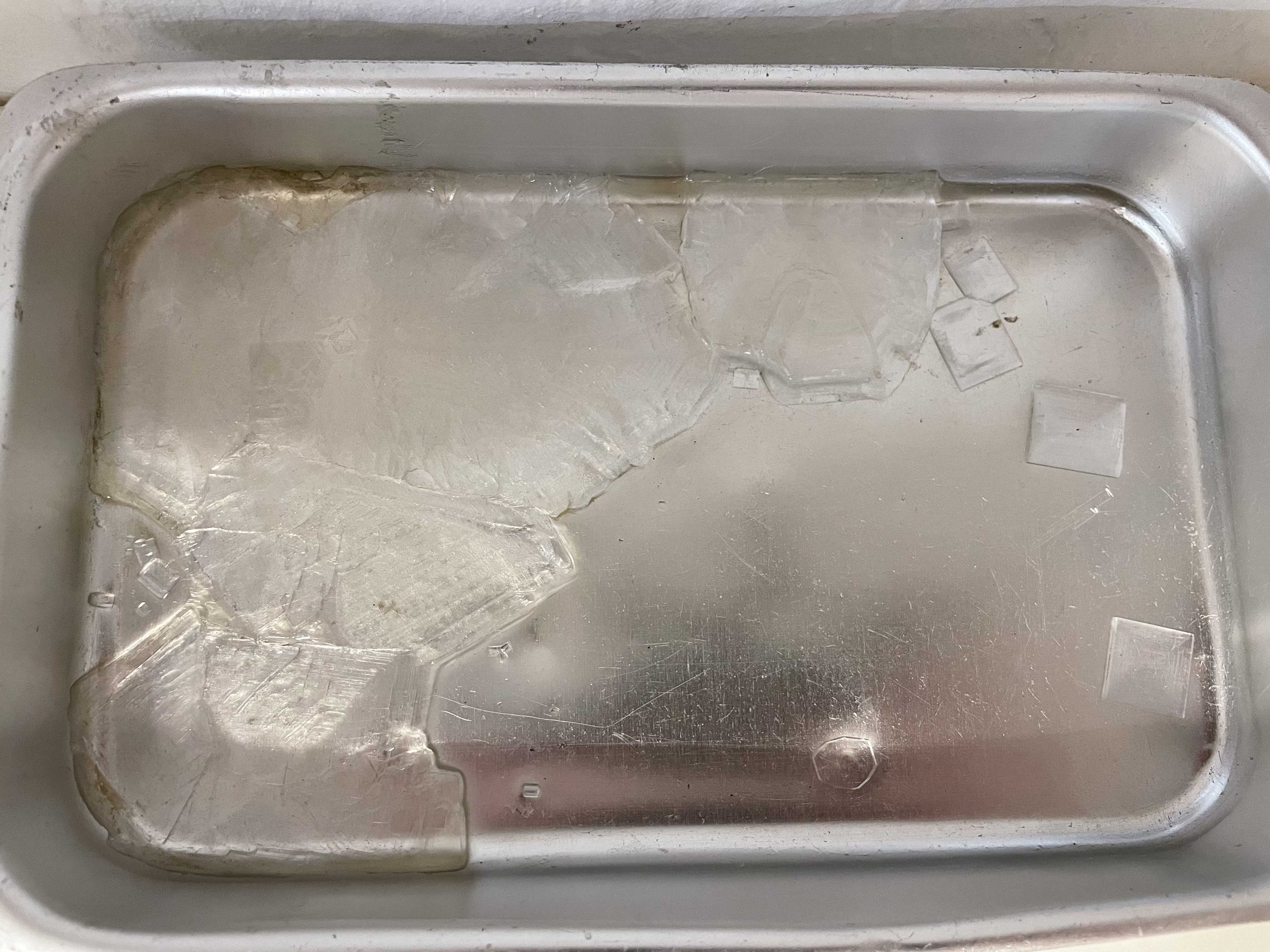
- Filter the solution through a coffee filter and the rest pour into a flat pan or plate to crystallize. Do not forget to cover it with a piece of ppaper to avoid dust.
- Usually it takes 2 days to grow crystals.
- After you can dry them naturally or use a dehydrator for 2O min 30°C and crush them into small pieces so you can use them to mix with copper sulphate.
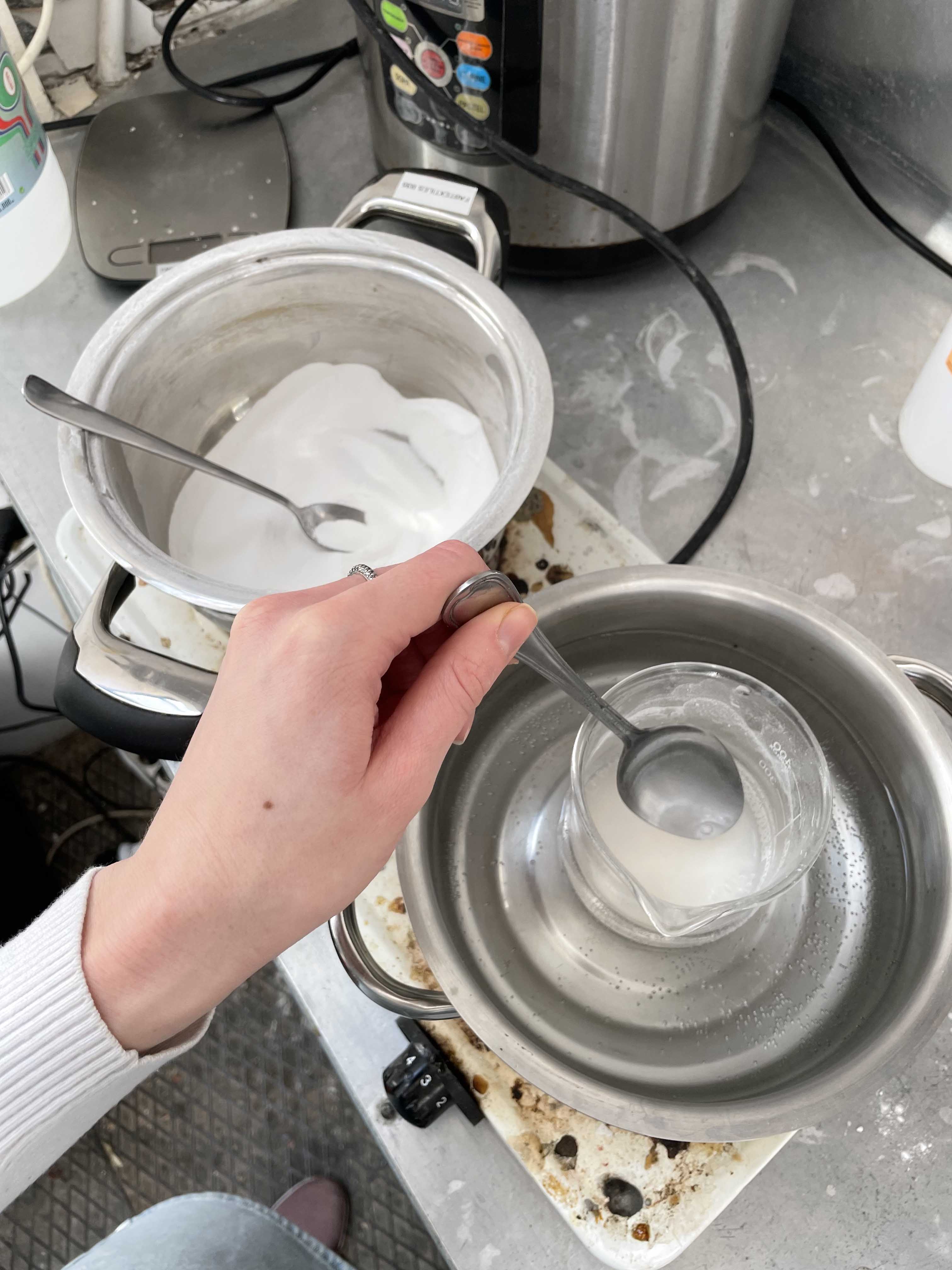
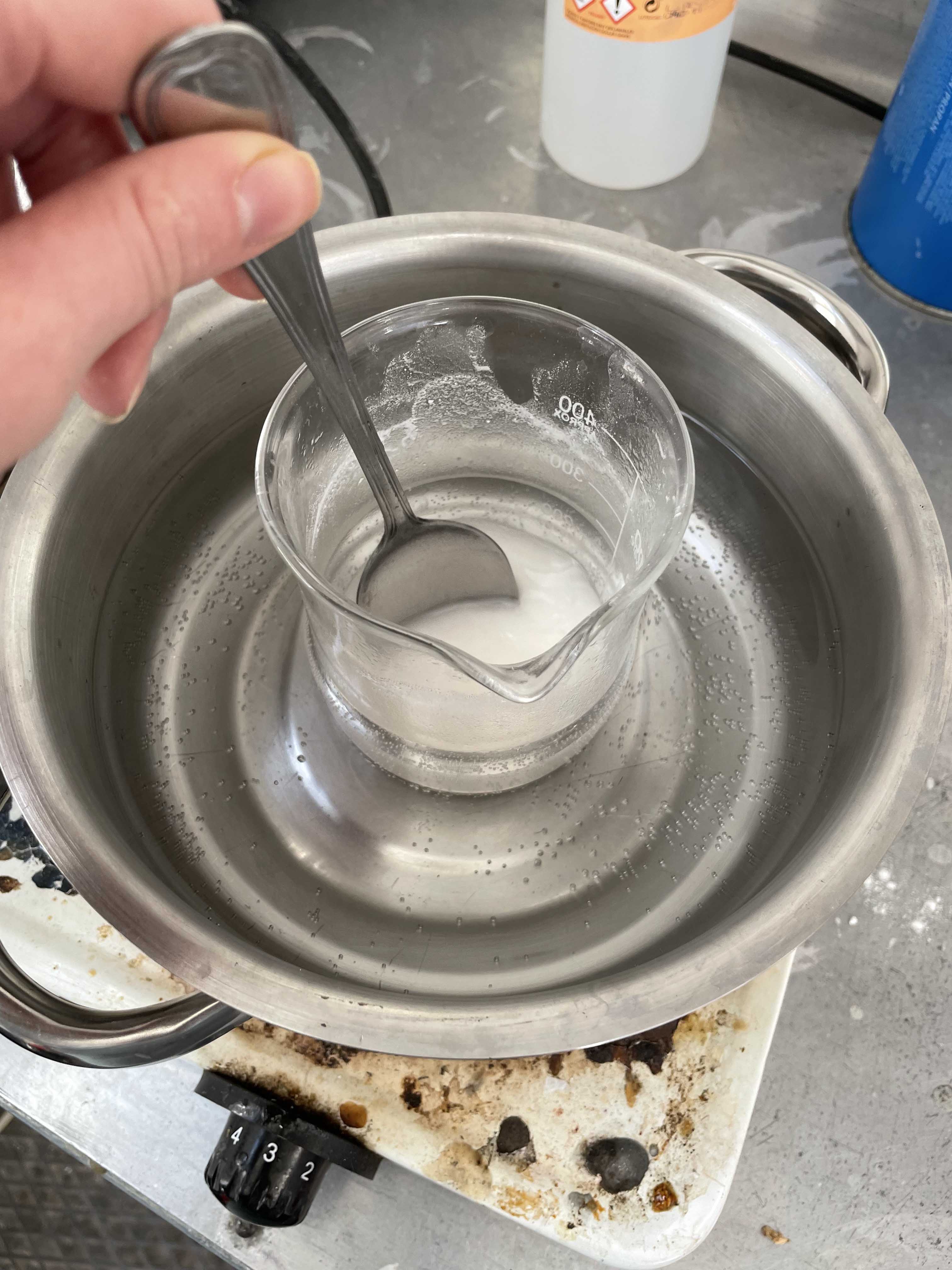




Crystallizing



Pricing
| n. |
Name |
Price |
Amount |
Source |
| 01 |
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) |
4,10 € |
1 kg |
Quimics Dalmau BCN |
| 02 |
Distilled water |
3-5 € |
5 l |
Fablab BCN |
| 03 |
Copper sulphate |
7,60 € |
1 kg |
Quimics Dalmau BCN |
| 04 |
Baking soda |
1,90 € |
1 kg |
Quimics Dalmau BCN |
| 05 |
Cream of tartar |
12,20 € |
1 kg |
Quimics Dalmau BCN |
| TOTAL |
- |
29,80 € |
- |
- |
Result
Conclusion
REFERENCE
6. DIALYSIS
| Timing |
Difficulty |
Safety |
| 2-3 days |
Medium |
Low |
- gloves, measuring glass cup, rubber band, cutter / scissors
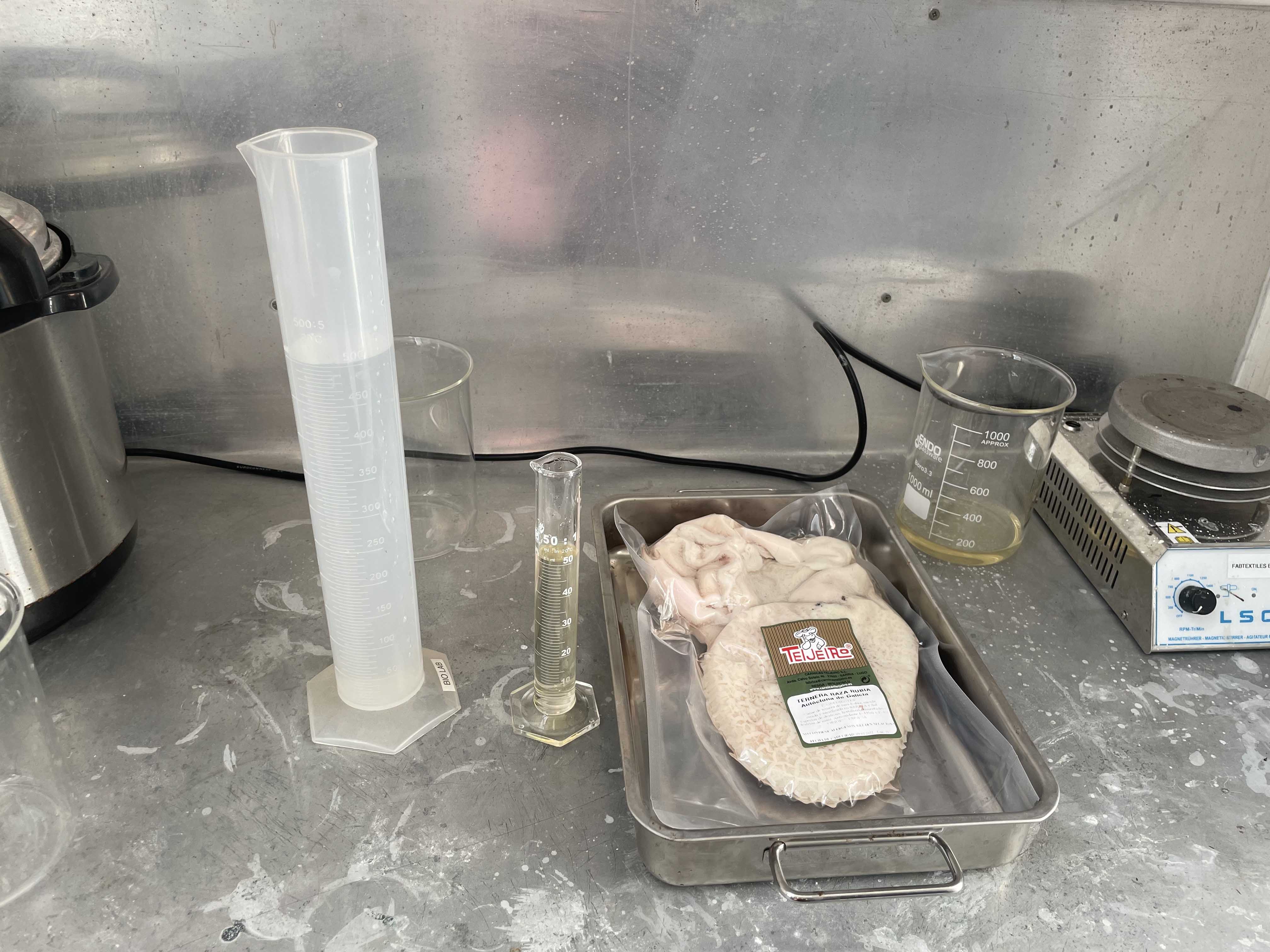
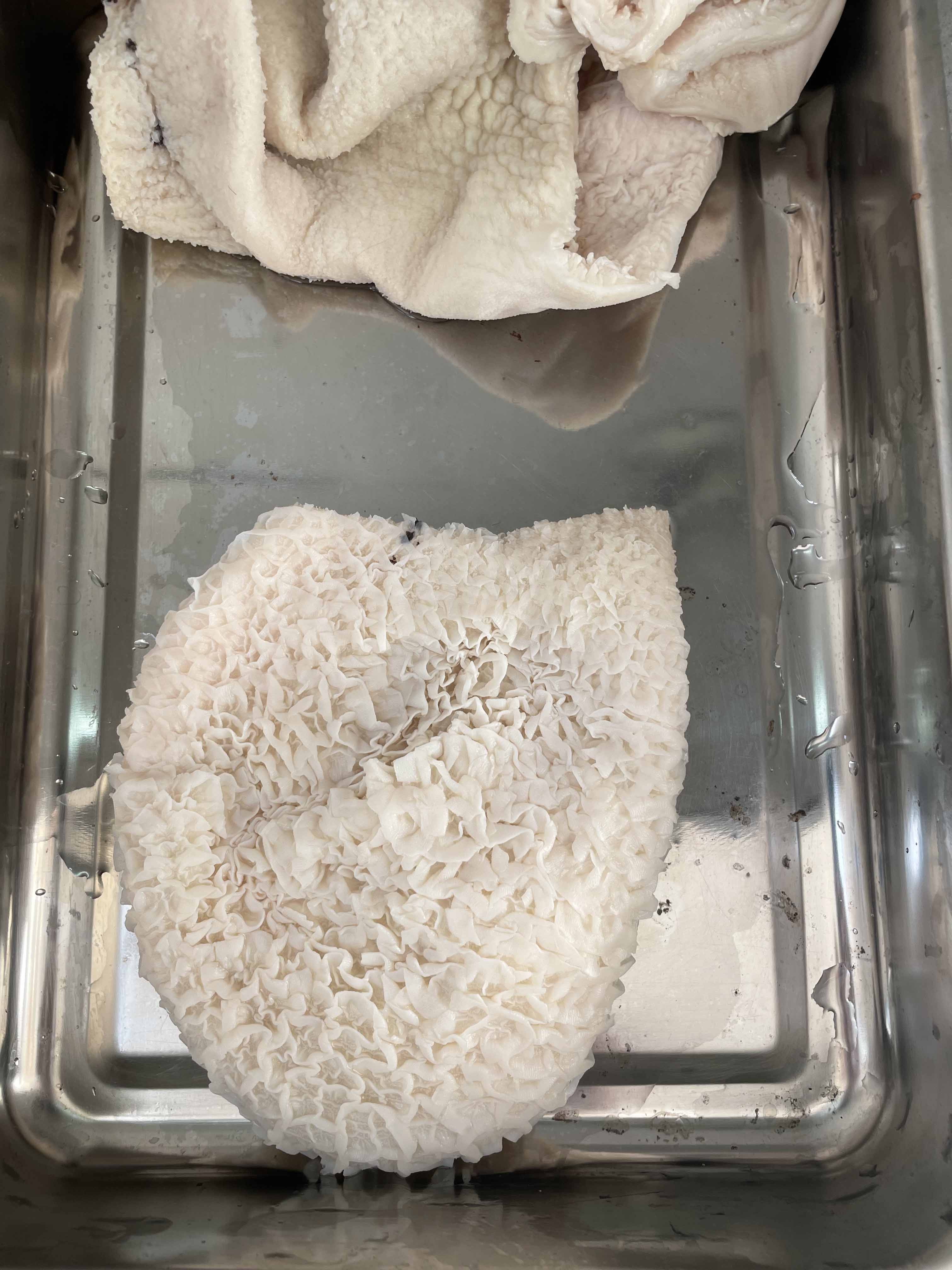
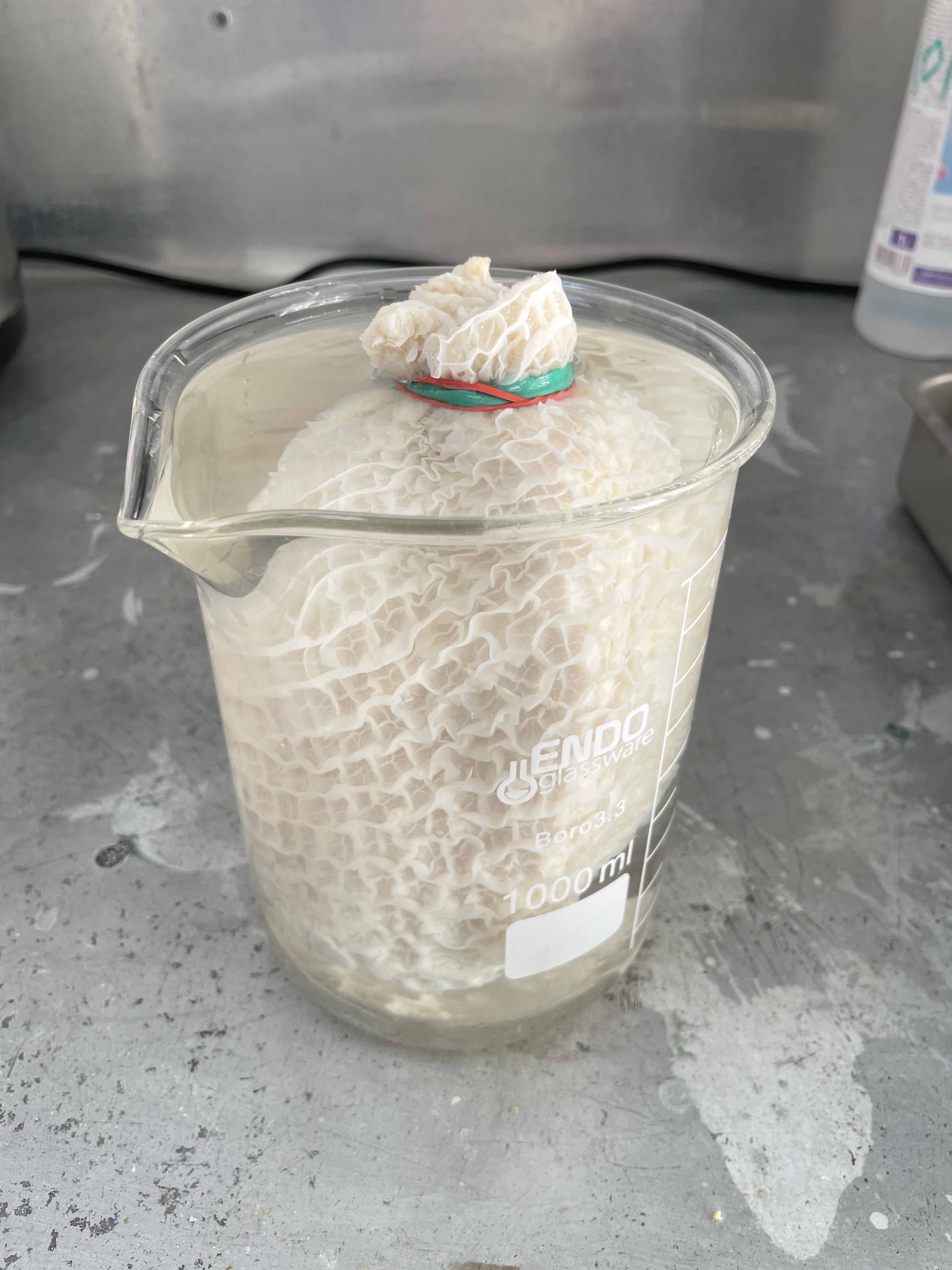




Materials
| n. |
Name |
Price |
Amount |
Source |
| 01 |
Cow intestines (stomach) |
16,59 € |
1 piece |
Cárnicas Teijeiro, Galícia |
| 02 |
Distilled water |
3-5 € |
5 l |
Fablab BCN |
| TOTAL |
- |
20 € |
- |
- |
Process
Conclusion
- You have to select a proper glass jar for the dialysis regarding to the size of animal intestines. It will need enough space and water around your "dialysing" membrane.
7. HYDROGEL PREPARATION
| Timing |
Difficulty |
Safety |
| 6 h |
Low |
Low |
- gloves, measuring glass cup, rubber band, cutter / scissors
Composition
| a. |
b. |
| Extraction |
Glycerol |
| 90 % |
10 % |
Process
7. CONCLUSION
| n. |
Activity |
Price |
Timing |
Difficulty |
Safety |
| 01 |
Wool composition |
x € |
24 h |
Low |
Low |
| 02 |
Chemical extraction |
x € |
6 h |
Medium |
High |
| 03 |
Filtration |
x € |
1 h |
Low |
Low |
| 04 |
Centrifuge |
x € |
15 min |
Low |
Medium |
| 05 |
Biuret testing |
x € |
50 h |
Medium |
Low |
| 06 |
Dialysis |
x € |
72 h |
Medium |
Low |
| 07 |
Preparation of hydrogel |
x € |
6 h |
Low |
Low |
| TOTAL |
- |
6 d 15 h 15 min |
- |
- |
|
Last update: 2022-05-10