9. Soft Robotics¶
Research and Ideation¶
I had never worked with soft robotics before. Although the concept was not very foreign, there was still a lot of variables that I had not experimented.

References & Inspiration¶
Intro to Soft Robotics Workshop for How to make (almost) anything 2019 has a nice summary, tips, tools and resources for making soft robotics.

I could not get to a point where I can test origami type of soft robotics this week. However, I really would like to test with origami actuation methods in the future. This paper has very nice experiments such as the ones below:
Weaving with soft robotics is also a nice way to control and observe the behaviour of the system. I have tried this method, however it is yet to work in a way that I am pleased. Here is the insipiration behind my interest in this combination.
Tools¶
Machines
- Cricut Maker 3
- Laser Cutter
- Heat Press
- Air pump
- 3D printer
Materials
- Heat press vinyl
- Baking paper
- TPU sheet
- Ecoflex 00-30
- PLA filament
- Gelatine
- Glycerine
Process and workflow¶
This week, we explored three methods of making soft robotics:
- Heat press vinyl
- TPU laser cutter welding
- Casting silicone / gelatine in PLA molds
Heat press vinyl¶
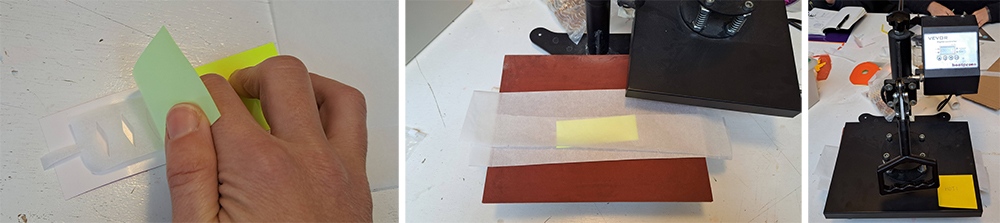
You can create a soft robotic actuator by heat pressing two heat press vinyls back to back with a baking paper that is cut in the shape of the air channels inside. A few important notes:
- Values of the heat press machine: 140 degree celcius and 15 second.
- Baking paper should indicate an outlet for pumping air inside.
TPU laser cutter welding¶
TPU is a thermoplastic which melts with heat. Using this property of TPU, you can weld two layers of TPU sheets together via using laser cutter out of focus.
We did a few test with our samples and the following are the values that worked best for our TPU and laser cutter (please be aware that the values may differ from machine to machine as well as different sheets of TPU):
| Operation | Laser head height | Speed | Power max | Power min |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Welding | 38 mm | 80 | 40 | 10 |
| Cutting | 5 mm | 100 | 35 | 10 |
You basically unfocus your laser lens by moving the laser head further away from th surface of your material. The welding operation results in a thicker outline than cutting. Therefore it is important to account for this thickness when designing. It is also a good idea not to bring any two lines closer than 5 mm.

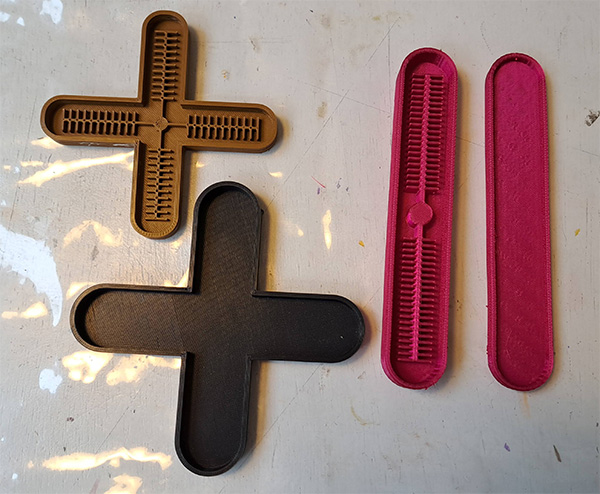
Casting silicone / gelatine in PLA molds¶
We made two types of soft actuators by molding and casting: bending and gripping.
We used the PLA mold for the gripping actuator we found at the FabLab that belonged to Samson, a Fab Academy student from the previous year. Looking at his documentation, he used this model to print the mold.
We printed the PLA mold for the bending actuator that was made Fabricademy 2022 by Saskia Helinska.

Casting with silicone¶
Silicone is made by mixing equal amounts of Part A and Part B of the Ecoflex 00-30. The mixture starts curing in 45 minutes so you should cast it before then. The whole curing process takes 4 hours afterwards. Silicone requires a cool room temperature to cure properly. After curing the parts, you prepare a small amount silicone mixture to apply a thin layer to bring together the two parts. You again need to wait 4 hours.

I had the pleasure of buying the new bottles Ecoflex 00-30 for the lab. The person at the store gave me very usuful tips about casting silicone:
- Best method of removing air bubbles from your mixture is to use a vacuum chamber. If you do not have it, vibration works to a certain extent.
- You can reduce bubble formation by folding the mixture rather than whisking it to mix.
- You really need to mix both parts really well. In order to ensure that, they suggest coloring one of the parts before mixing them. You need to use a a specific type of color for this. Color helps with visual cues of mixing. The other suggestion is after mixing them well, pour them thoroughly in another container and mix again. This ensures that the bottom of the first container is totally sweeped into the second container and mixed well.
- Pour your mixture on the mold where it is the deepest and let the mixture move slowly to fill empty volume. This helps eliminating air traps.
- Start pouring from a close height but move the container further higher (as high as you are comfortable). This makes the pouring mixture thin down and help with getting rid of air bubbles.
![]()
Casting with gelatine¶
We made a mixture of gelatine with glycerine to make a biodegradable material to cast in the molds.
The ingredients are:
- 500ml water
- 100 gr powder gelatine
- 100 gr liquid glycerine
- mica powder (not mandatory - just to add some color to the material)
We observed that gelatine mixture is more brittle and did not even come out of the pink mold beacuse the pink mold had an irregular inner surface.
We also could not bring the two parts together with the same mixture. This experiment still needs more adjustments to work but definetely worth pursuing because of the biodegradability aspect compared to the silicone robotics.

Personal tests¶
I wanted to experiment with several methods for my personal projects
Casting in acrylic molds¶
I prepared an acrylic mold in Rhino and cut in the laser cutter. You need at least 5 layers of acrylic layers for this to work. This soft robot also has two parts that need to be glued together afterwards. You can download the files here1.
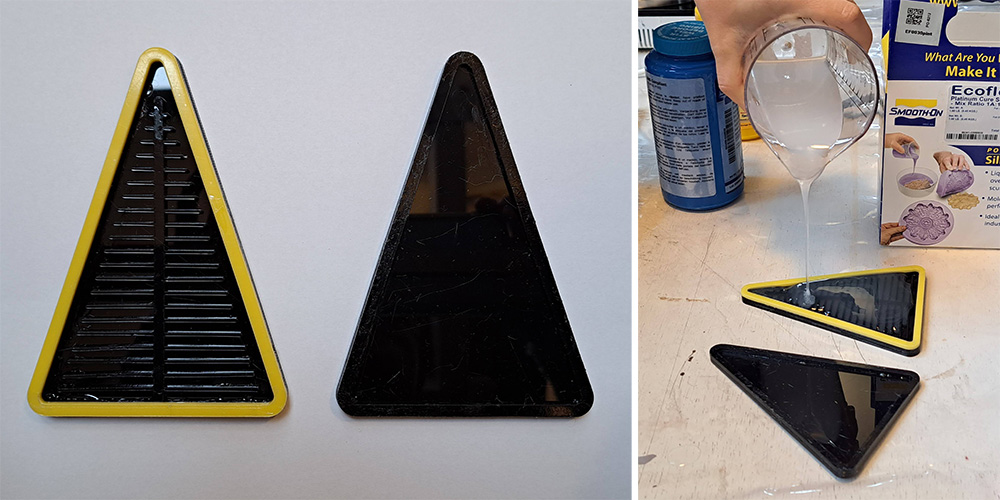
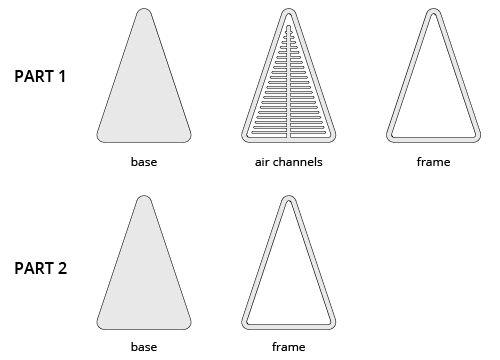

There was a lot of unglued parts and also popped parts in this piece, so I cut away the part with the problems and inflated to see the effects again.
The air coming out of the compressor is still too much that the parts popped again at the end but I was able to observe the bending effect of this design.
Weaving with inflatables¶
I was very inspired from the Active Textile Made of Thin McKibben Muscles. Instead of making McKibben muscles (it would take a long time to outsource the materials), I made channels for airflow and cut them from heat press vinyl and baking paper in Cricut Maker 3. You can download the file here2. Later, I brought the pieces together in the heat press. You can also use the same file in the laser cutter to weld TPU. The baking paper outline should be in welding values in laser cutter and the vinyl should be in cut values.
I used a frame loom and cotton thread as warp. I wove in twill weave structure.
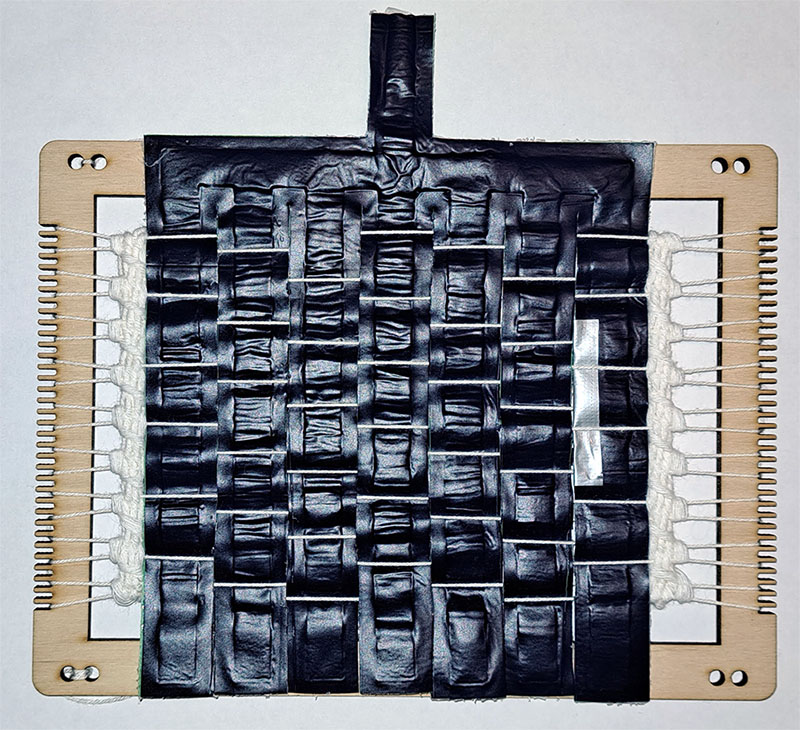
The actuated shape of the structure looks like a barrel vault that keeps the vertical channels straight and the horizontal channel bent.
I also tried weaving two vinyls in twill weave.
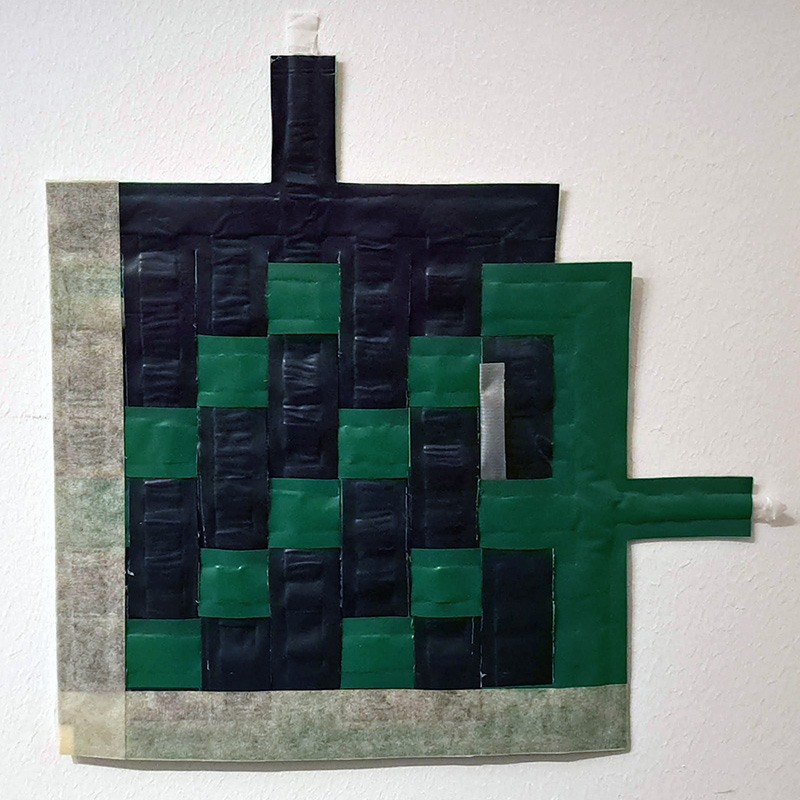

Unfortunately, it is really hard to keep one of them inflated and then inflate the other one by myself. So that part still needs experimentation. I am curious of the results.
Bending and twisting¶
I made several experiments with vinyl to see the effects of pattern on the movement performance of soft robotics. You can download the files here3.

Notes from the Classroom¶
notes from the classroom
SOFT ROBOTICS lecture by Lily Chambers
Soft robots need soft actuation
soft robots are systems that are compliant and flexible. have a feedback sensory and control system.
stimuli for soft actuators: fluidic, chemical, biological, thermal, electrical, magnetic, hybrid systems
soft actuators are systems that are compliant and flexible. can be used for shape changes, joining and locomotion.
Fluid actuated: pneumatic PneuNets (bending actuators), Bio-inspired octopus robot, pneubotics, foam (fluid-driven origami-inspired artifical muscles), furl - soft pneumatic pavillion (interactive archtecture lab), aposema - soft robotic mask (interactive architecture lab)
Chemically actuated: octobot
Thermal actuated STAT (smart thermally actuatind textiles) - wyss institute
Electral actuated electroactive polymers. ionic metal polymer composites, field activated electroactive polymers (dielectric elastomers), electroactive threads (weaving and knitting, with tunable force and strain)
Active textile made of thin mckibben artificial muscles.
Cellulose 'paper' actuation - swelling and drying. fiber alignment
Gelatine fabricated actuators
SOFT ROBOTICS lecture by Adriana Cabrera
Compliance - bend, squish, stretch, silkiness, ...
artificial muscles
Fabrication files¶
-
File: acrylic mold ↩
-
File: bending and twisting ↩

