5. E-Textiles¶

GLOSSARY¶
Important terms to remember.
-
Circuit: a roughly circular line, route, or movement that starts and finishes at the same place.
-
Current: electrical conductor or space. It is measured as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface or into a control volume.
-
Electricity: is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations.
-
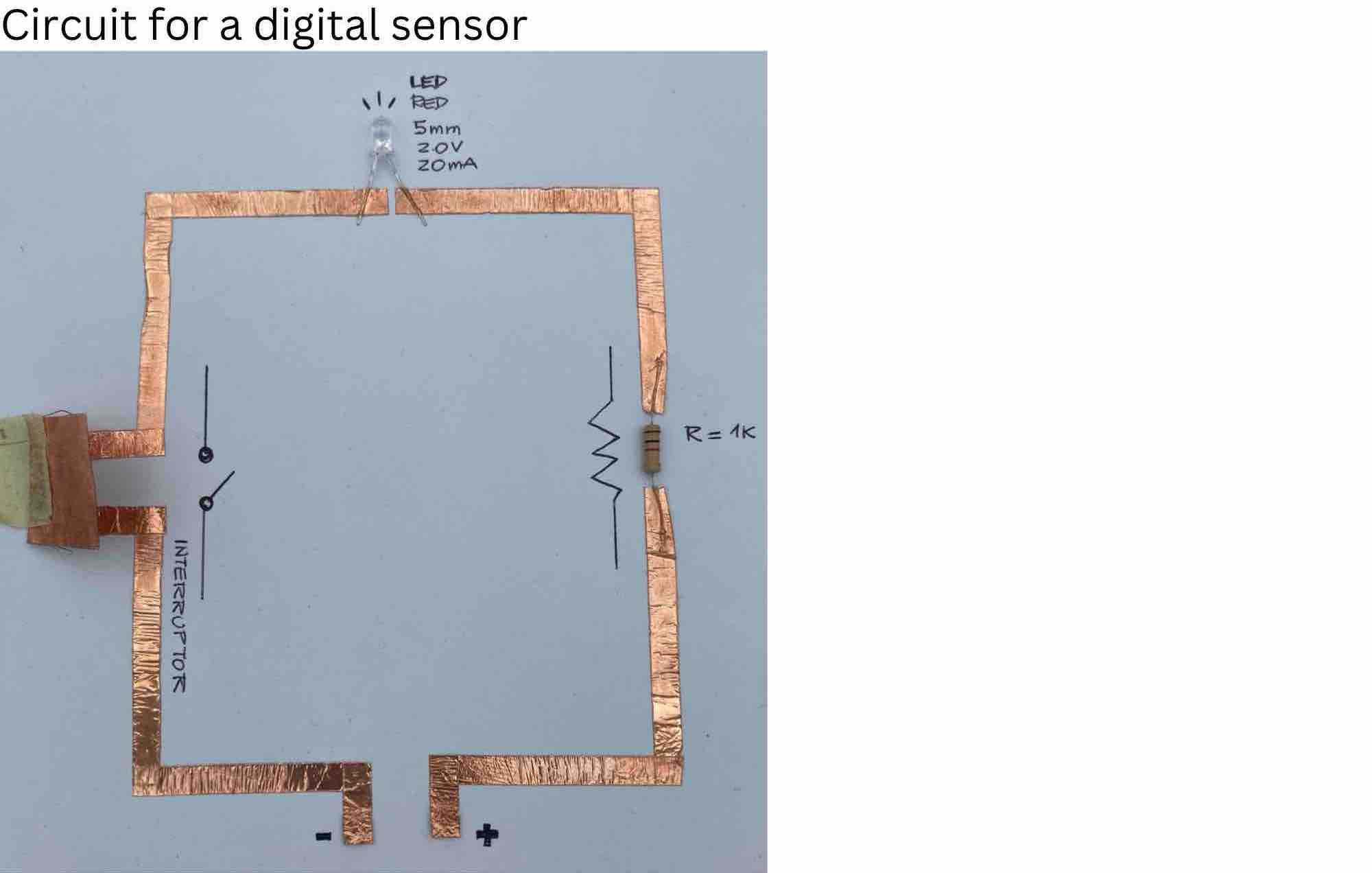
Electronic circuit: is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow.
-
Ground: In electrical engineering, ground or earth is a reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth. Electrical circuits may be connected to ground for several reasons.
-
Power: ability to act or produce an effect.
-
Resistance: is an electrical quantity that measures how the device or material reduces the electric current flow through it. The resistance is measured in units of ohms (Ω). If we make an analogy to water flow in pipes, the resistance is bigger when the pipe is thinner, so the water flow is decreased.
OHMS Law¶

References from Jessica Stanleys Lecture¶
-
Leah Buechley
 more info on LEAH BUECHLEY
more info on LEAH BUECHLEY -
Irene Posch + Ebru Kurbak
more info on IRENE POSCH &Ebru Kurbak
-
Kobakant
 Check out more here
Check out more here -
Jessica Stanley
¨Stitch Synth is an e-textile, modular, analog synthesizer. Developed between January and March 2019 as my graduation project for Fabricademy, a new textile and technology academy. Stitch Synth consists of 10 modules, made out of textiles, conductive textiles, and electronic components, that snap together to generate simple electronic sounds. With soft, expressive interfaces that allow the user to control the sound through touch, Stitch Synth explores how we interact with electronics, and how the musical instruments of the future might look. All circuitry in Stitch Synth is exposed and incorporated into the design, making the electronics visible rather than hiding it in a black box. Motivated in part by the optimistic and geometric design of the ‘Space Age’, and by a desire to make electronics more accessible¨
- Handmade Electronic Music by Nicholas Collins

PRIMARY TOOL¶

A multimeter or a multitester, also known as a volt/ohm meter or VOM, is an electronic measuring instrument that combines several measurement functions in one unit. A typical multimeter may include features such as the ability to measure voltage, current and resistance.:
- Voltage, alternating and direct, in volts.
- Current, alternating and direct, in amperes.
- Resistance in ohms.
TYPES OF CIRCUITS¶


Notes on ENERGY¶

Process and workflow¶
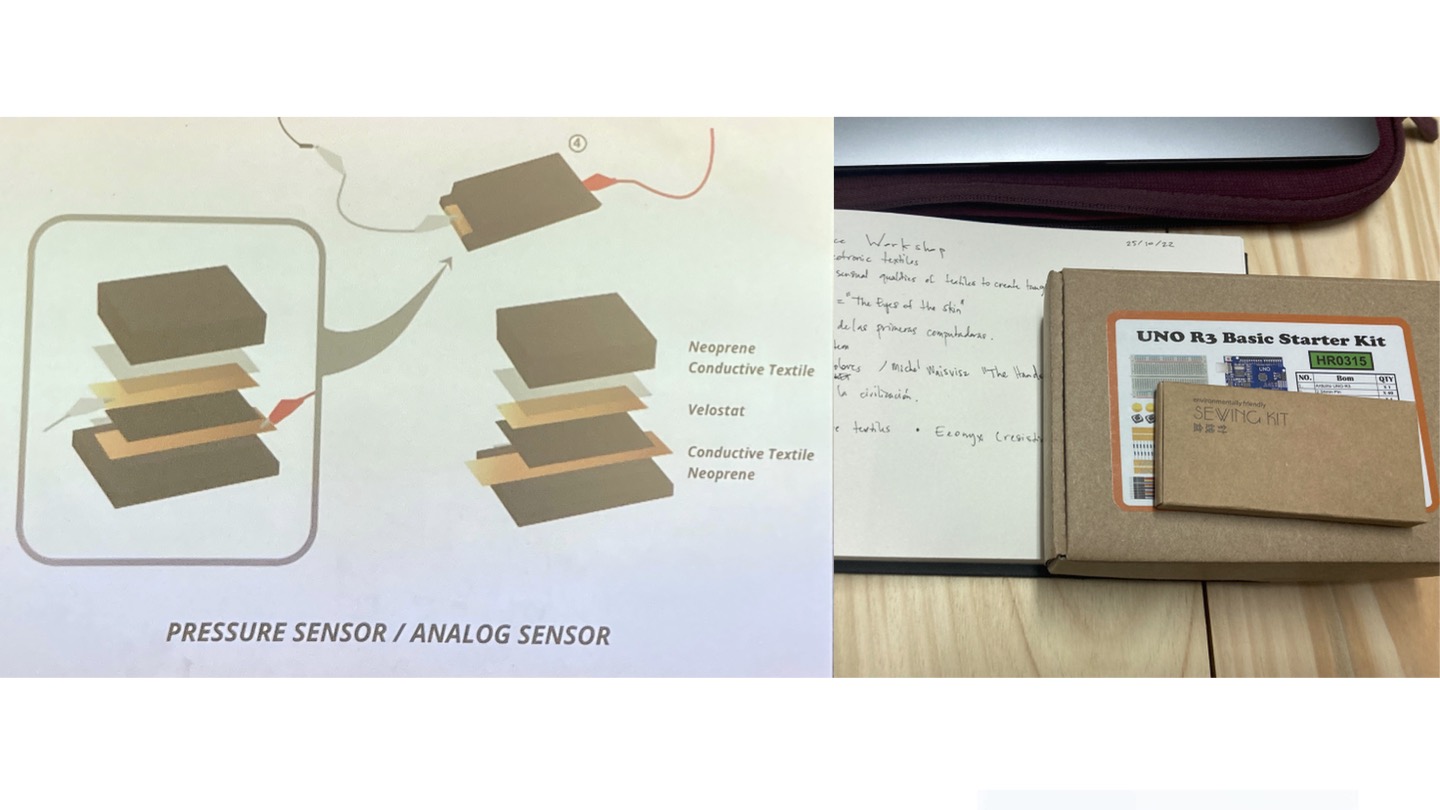
Simple visual explanation on how to prepare for the digital sensor which you´ll see functioning in the video/gif below in two formats sensor 1 sensor 2:
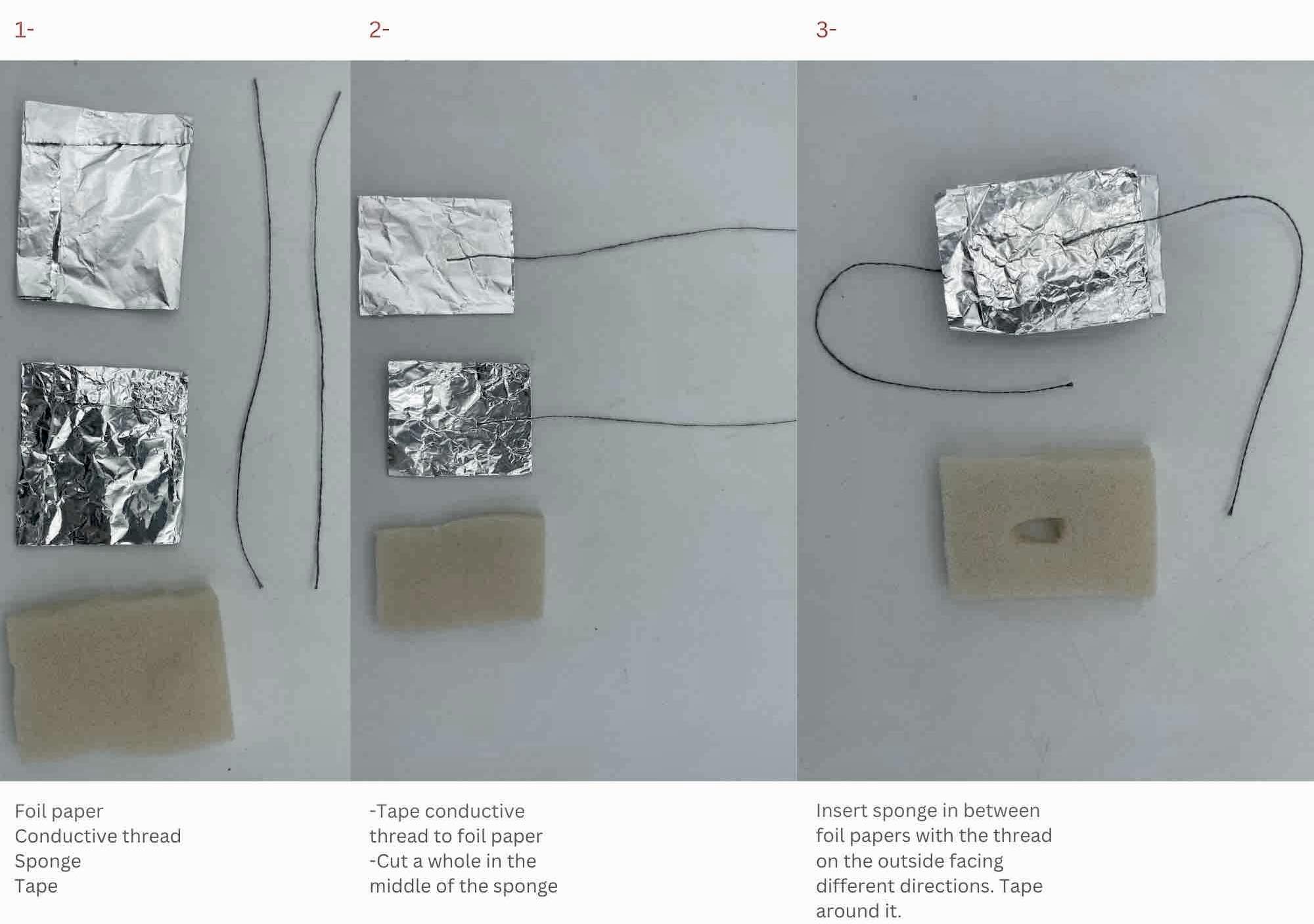
TYPES OF SENSORS¶

Visual Aid of results¶
Digital Sensor 1; light¶
Digital Sensor 2; sound¶
Arduino codes AnalogA Digital B¶
int analog_sensor_pin = A0; //change the pin, where the sensor is connected?
int analog_sensor_value = 0;
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
pinMode(analog_sensor_pin, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
analog_sensor_value = analogRead(analog_sensor_pin); //read the Voltage of the pin sensor
Serial.println(analog_sensor_value); // print the value on the Serial monitor
delay(100);
}
digitalWrite(led_pin, HIGH); // turn the LED on
delay(100);
digitalWrite(led_pin, LOW);
delay(100);
---¶
Skinterface Workshop with EJTECH¶
Because I anticipated the complexity of understanding the high tech assignments, I went ahead and signed myself for a workshop outside. I got quite lucky as the workshop was being delivered by tech genius EJTECH Esteban de la Torre.
EJTECH is an interdisciplinary artistic duo who work with hyperphysic interfaces, programable material and augmented textiles with medium to investigate the sensorial and conceptual relationships between subject and object with the objective of redescovering emerging structures within realism and metamaterialism. Sound, space, light and time as construction blocks are primary elements in their practice. They analize patterns of develpment processes between technology and the human body. Driven by material investigation, which result in performative instalations, multi channel sonic sculptures and dynamic surfaces. They are highly influenced by the philosophy of New Materialism, Holonic Theory and Somoaesthetic.
ART +: EJTech Studio from Gheada on Vimeo.
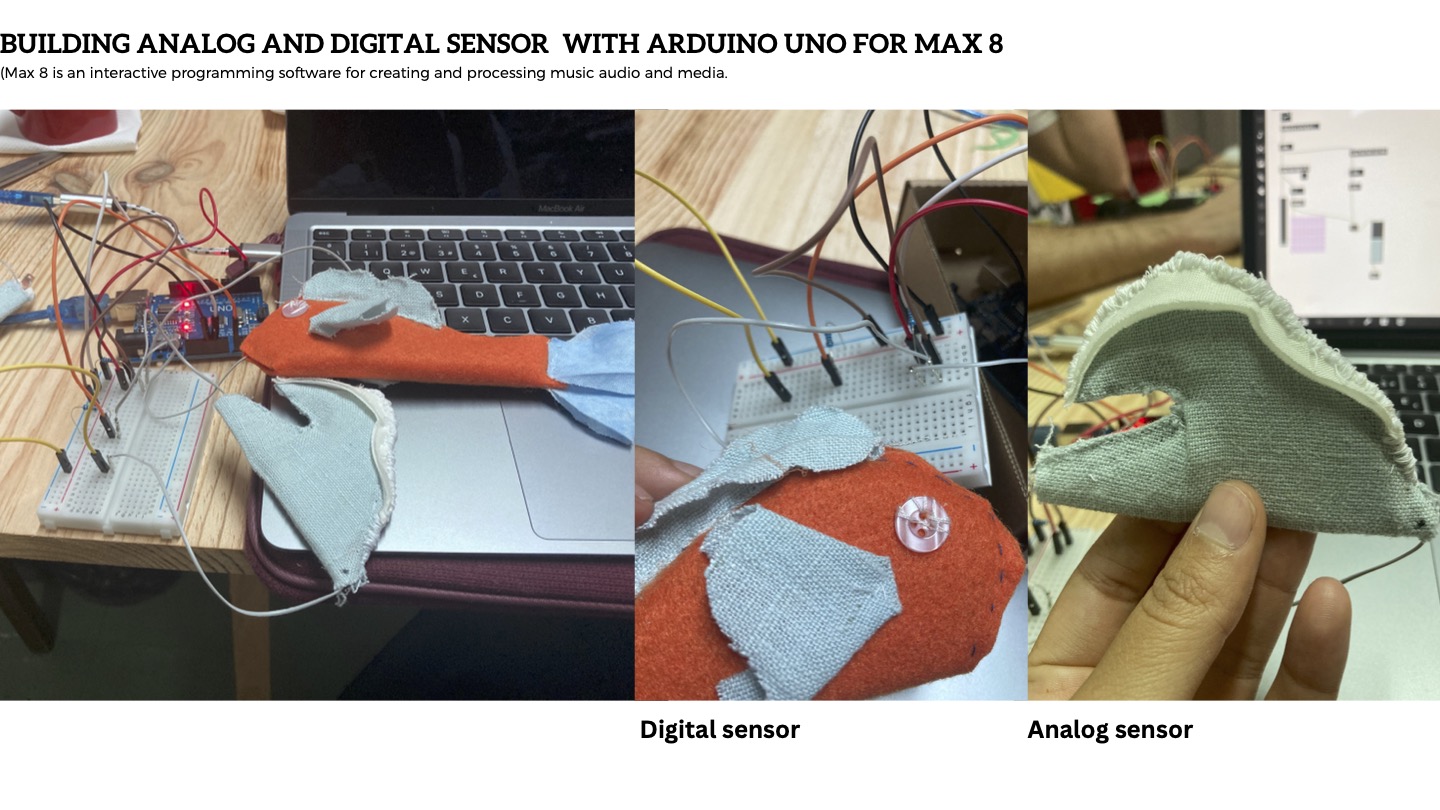
The objective of the workshop was to develop a digital and analog sensor to be used with a interactive audio program for the creation of a personal melody or tune called MAX 8
Digital Sensor 3; button for melodies.¶
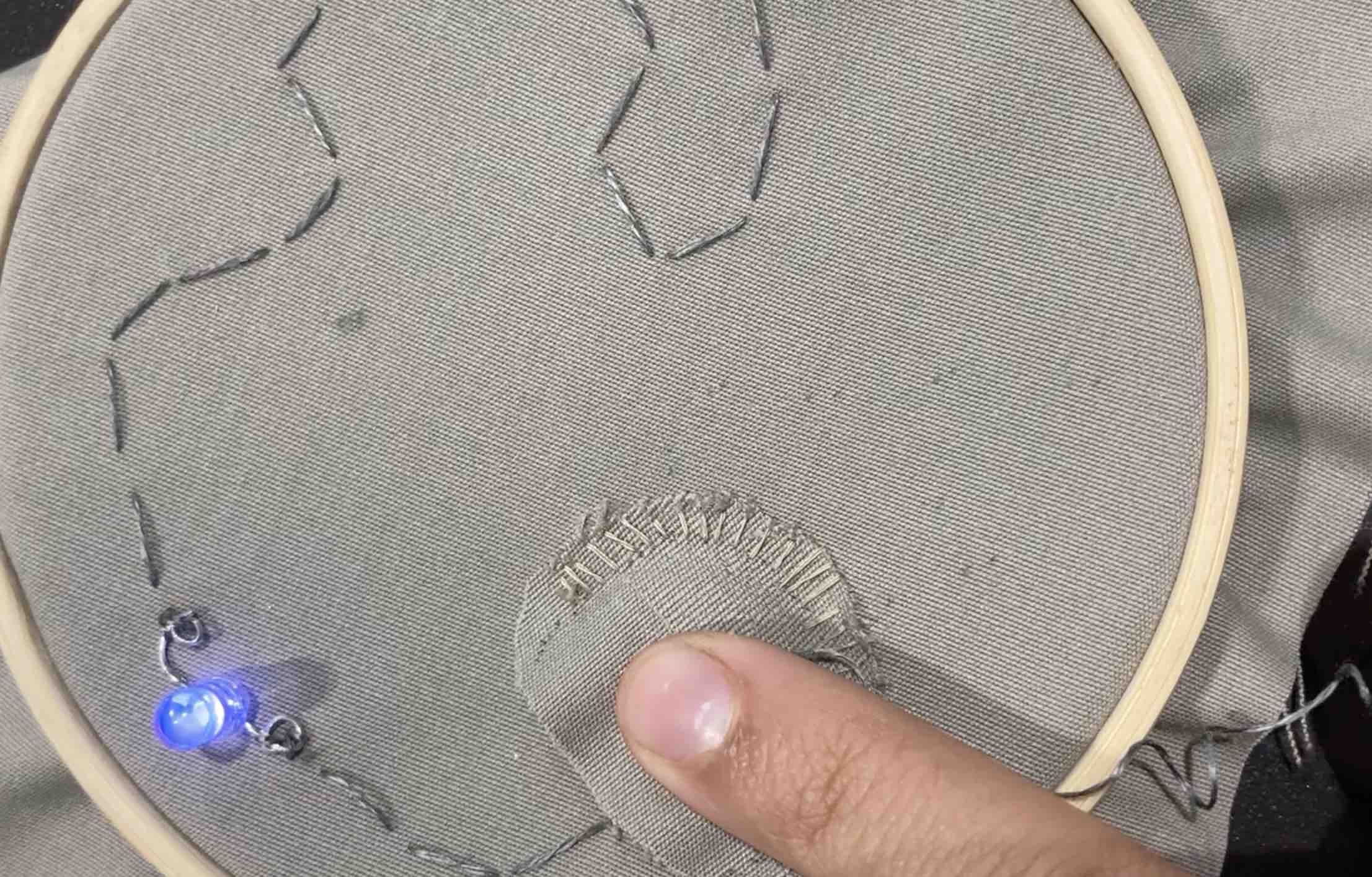
After understanding the digital sensor I went ahead and made a small fish, in the video below you can see how I´m testing the digital sensor with the MAX 8 program. Essentially, the digital sensor as demonstrated below is a closed circuit of yes or no, there´s no range here, if you look closely into the interface, when I touch the fish it goes from 0 to 1.
Getting ready with Arduino and understanding Analog fabrication¶
Essentially, the analog wave button is also a closed circuit but with a reading range wider than a simple yes or no, so as you can see in the video below, depending on where I touch the "wave" and the pressure I apply, the interface Max 8 will read different sounds because it has the capacity of reading more than an open or closed signal.